

- Critical thinking enhances scientific research by allowing researchers to rigorously question assumptions, formulate testable hypotheses, and design reliable experiments that lead to new discoveries.
- Questioning assumptions is crucial in business because it helps leaders avoid blind spots, explore alternative strategies, and make decisions based on well-rounded, critical analysis.
- In legal case analysis, critical thinking allows lawyers to evaluate evidence thoroughly, anticipate opposing arguments, and present a logically sound case.
- Cognitive biases hinder critical thinking, and strategies like self-reflection and seeking out diverse perspectives can help mitigate their effects.
- In technology, critical thinking helps technologists assess the ethical implications of their innovations, consider potential societal impacts, and make responsible choices in developing new technologies.
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Describe the positive feedback loops between critical thinking and other domains of inquiry.
- Provide ten scenarios that demonstrate the synergistic relationship between critical thinking and other disciplines.
- Create a graph that quantitatively shows the degree of utility of critical thinking in various disciplines.
- Provide a framework for a regular diet of critical thinking content.
- Quiz
- Provide 20 discussion questions relevant to the content above.


Describe the positive feedback loops between critical thinking and other domains of inquiry.
Introduction
Critical thinking is the disciplined process of actively conceptualizing, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information to reach an informed conclusion. It involves open-mindedness, skepticism, and a rational approach to problem-solving. Other domains of inquiry—such as science, mathematics, humanities, and social sciences—rely heavily on critical thinking skills. Conversely, engaging deeply in these domains further hones one’s critical thinking abilities. This reciprocal enhancement creates positive feedback loops, where improvements in one area reinforce and amplify advancements in the other.
Critical Thinking Enhances Domains of Inquiry
- Scientific Advancement
- Hypothesis Formation: Critical thinking allows scientists to formulate testable and meaningful hypotheses by questioning existing knowledge and identifying gaps.
- Experimental Design: Evaluating the validity and reliability of experimental setups requires logical reasoning and the ability to anticipate potential flaws.
- Data Interpretation: Analyzing complex data sets to draw accurate conclusions necessitates discerning patterns and relationships critically.
- Example: The development of the theory of relativity required Einstein to critically assess the limitations of Newtonian physics, leading to groundbreaking advancements.
- Mathematical Problem-Solving
- Logical Reasoning: Mathematics is rooted in logical structures; critical thinking enables mathematicians to follow and construct rigorous proofs.
- Abstract Thinking: Dealing with abstract concepts requires the ability to think beyond concrete examples and consider broader implications.
- Example: Solving Fermat’s Last Theorem involved deep critical analysis of existing mathematical principles over centuries.
- Humanities and Social Sciences
- Textual Analysis: Interpreting literature or historical documents demands careful evaluation of language, context, and subtext.
- Ethical Reasoning: Philosophical inquiries into morality require weighing complex arguments and considering multiple viewpoints.
- Example: Debates on ethical issues like artificial intelligence involve critical assessments of potential societal impacts.
Domains of Inquiry Enhance Critical Thinking
- Complex Problem Engagement
- Engaging with challenging problems in any domain forces individuals to apply and refine their critical thinking skills.
- Example: Tackling a complex engineering problem requires the integration of theoretical knowledge and practical constraints, enhancing problem-solving abilities.
- Interdisciplinary Connections
- Exploring different fields encourages the application of critical thinking across contexts, strengthening cognitive flexibility.
- Example: Understanding economic trends may involve statistical analysis (mathematics), human behavior (psychology), and policy implications (political science).
- Feedback from Outcomes
- Observing the results of inquiries provides feedback that reinforces or challenges existing thought processes.
- Example: A failed experiment leads a scientist to reassess their hypotheses and methodologies, deepening their critical evaluation skills.
The Positive Feedback Loop
- Reinforcement Cycle: As critical thinking enhances one’s ability to engage deeply in a domain, the challenges encountered within that domain further sharpen critical thinking skills.
- Example: A student learns critical thinking techniques in a logic course, which improves their performance in analyzing historical events. This deeper historical analysis then presents new complexities that require even more advanced critical thinking.
- Increasing Complexity and Depth
- Mastery in a domain often leads to exploring more complex issues, necessitating higher-order critical thinking.
- Example: An economist who understands basic market principles may delve into complex models predicting economic crises, requiring advanced analytical skills.
- Innovation and Creativity
- Critical thinking fosters innovation by enabling individuals to question norms and think outside the box.
- Engaging in innovative work provides new challenges that further develop critical thinking.
- Example: Tech innovators use critical thinking to disrupt existing technologies, and the process of innovation presents new problems to solve, enhancing their analytical abilities.
Conclusion
The interplay between critical thinking and other domains of inquiry is a dynamic and reciprocal relationship. Critical thinking skills enable deeper engagement and breakthroughs in various fields. In turn, the complexities and challenges of these fields provide fertile ground for honing critical thinking abilities. This positive feedback loop not only advances individual competence but also drives collective progress across disciplines, leading to intellectual growth and the advancement of knowledge.
Provide ten scenarios that demonstrate the synergistic relationship between critical thinking and other disciplines.
1. Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
Scenario:
A physician encounters a patient with a set of unusual symptoms that do not align neatly with any known disease. By applying critical thinking, the doctor questions initial assumptions, considers rare conditions, and evaluates the patient’s history in depth. This thorough analysis leads to the identification of a rare autoimmune disorder.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Medicine: The physician’s critical evaluation leads to an accurate diagnosis, improving patient care.
- Medicine Enhances Critical Thinking: The complexity of medical cases challenges the physician to continually refine diagnostic reasoning skills.
2. Engineering Design Innovation
Scenario:
An engineer tasked with designing a sustainable building questions traditional architectural methods. By critically assessing materials and energy consumption, they develop an innovative design that utilizes renewable resources and reduces the carbon footprint.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Engineering: Questioning conventional practices leads to innovative solutions.
- Engineering Enhances Critical Thinking: Complex design challenges require the engineer to enhance problem-solving strategies.
3. Literary Analysis and Interpretation
Scenario:
A literature student critically examines a classic novel, exploring underlying themes of societal oppression and individual freedom. By challenging traditional interpretations, the student uncovers a new perspective on the author’s intent.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Literature Studies: Deep analysis leads to a richer understanding of the text.
- Literature Studies Enhance Critical Thinking: Interpreting complex narratives hones the student’s analytical and interpretative skills.
4. Scientific Research and Hypothesis Testing
Scenario:
A biologist observes anomalies in cell behavior that contradict existing theories. Through critical analysis, they formulate a new hypothesis about cellular mechanisms and design experiments to test it, leading to a potential breakthrough in understanding cell biology.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Science: Rigorous questioning and testing lead to scientific advancements.
- Science Enhances Critical Thinking: The scientific method requires and develops systematic analytical skills.
5. Legal Reasoning and Case Analysis
Scenario:
A lawyer preparing for a court case critically examines all evidence, questioning the reliability of witnesses and the validity of opposing arguments. This thorough analysis uncovers inconsistencies that are pivotal in winning the case.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Legal Practice: Detailed evaluation of evidence strengthens legal arguments.
- Legal Practice Enhances Critical Thinking: Legal analysis sharpens logical reasoning and argumentative skills.
6. Historical Research and Interpretation
Scenario:
A historian studies newly discovered documents from a past era. By critically assessing the sources and considering the context, they challenge existing historical narratives and provide a revised interpretation of significant events.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances History: Careful source evaluation leads to more accurate historical accounts.
- History Enhances Critical Thinking: Analyzing historical events develops the ability to assess evidence and context critically.
7. Business Strategy and Decision Making
Scenario:
A business executive faces declining sales. By critically analyzing market trends, consumer behavior, and internal processes, they identify underlying issues and develop a strategic plan that revitalizes the company.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Business: In-depth analysis leads to effective strategies and solutions.
- Business Enhances Critical Thinking: Complex business challenges require and develop strategic thinking skills.
8. Ethical Dilemmas in Technology
Scenario:
A software developer is asked to create an application that could infringe on user privacy. By applying critical thinking to assess ethical implications, they propose alternative solutions that balance functionality with ethical considerations.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Technology Development: Ethical evaluation leads to responsible innovation.
- Technology Development Enhances Critical Thinking: Navigating technological ethics sharpens moral reasoning and foresight.
9. Environmental Policy Formulation
Scenario:
An environmental scientist critically evaluates the impact of proposed legislation on ecosystems. By analyzing data and modeling outcomes, they advise policymakers to amend the legislation to better protect the environment.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Environmental Science: Detailed impact analysis leads to informed policy recommendations.
- Environmental Science Enhances Critical Thinking: Complex ecological considerations enhance analytical and predictive skills.
10. Artistic Expression and Critique
Scenario:
An artist critically reflects on societal issues and incorporates this introspection into their work. When presenting the art, they engage with critics and audiences, discussing themes and interpretations that provoke thoughtful dialogue.
Synergy:
- Critical Thinking Enhances Art: Deep reflection leads to meaningful and impactful artistic creations.
- Art Enhances Critical Thinking: Engaging with art stimulates analysis of themes, emotions, and societal issues.
Summary
In each of these scenarios, critical thinking empowers individuals to delve deeper into their respective disciplines, leading to innovative solutions, enhanced understanding, and improved outcomes. Simultaneously, the challenges and complexities inherent in these disciplines serve to sharpen and refine critical thinking skills. This synergistic relationship fosters continuous growth and development, benefiting both the individual and the broader field of inquiry.
Create a graph that quantitatively shows the degree of utility of critical thinking in various disciplines.
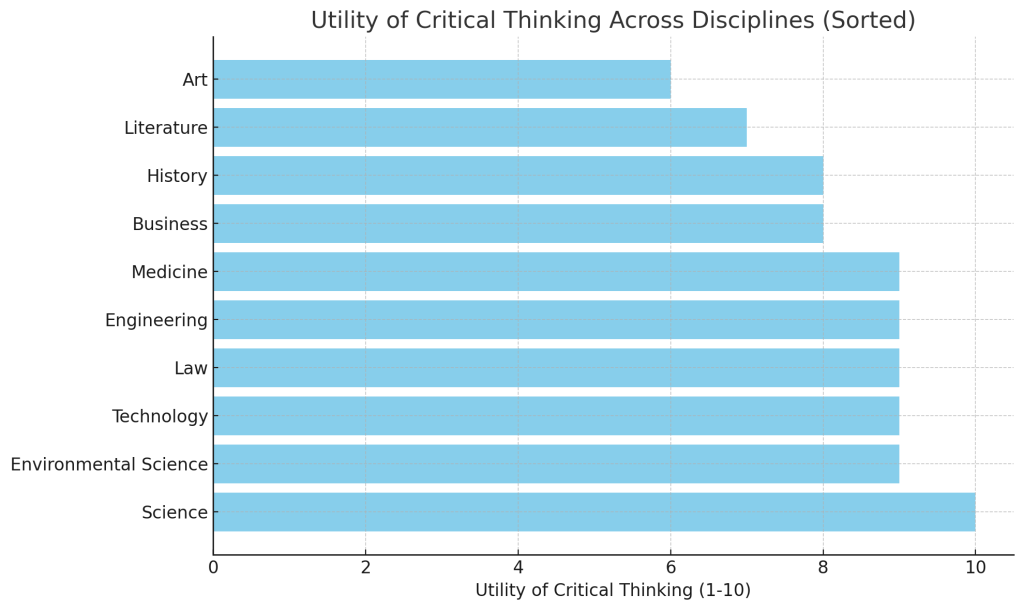
The graph above shows the degree of utility of critical thinking across various disciplines, with values on a scale from 1 to 10. Critical thinking plays a crucial role in fields like Science, Medicine, Law, and Engineering, with slightly lower but still significant importance in areas such as Literature and Art. The variation reflects how critical thinking enhances both practical problem-solving and interpretative reasoning in these fields.
Provide a framework for a regular diet of critical thinking content.
Framework for a Regular Diet of Critical Thinking Content
A well-rounded critical thinking regimen involves consistent exposure to diverse content that challenges assumptions, refines reasoning, and enhances analytical skills. Below is an extensive framework of books, podcasts, websites, and other media that can form the foundation of this intellectual diet.
I. Books
1. Philosophy and Logic
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
- Offers insights into how human reasoning works, covering both quick intuitive responses and slow, deliberate thinking.
- “An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding” by David Hume
- A classical work that introduces concepts of empiricism, skepticism, and the limits of human knowledge.
- “The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark” by Carl Sagan
- Explores the scientific method as a tool for critical thinking, especially when examining pseudoscience and superstitions.
2. Science and Inquiry
- “The Logic of Scientific Discovery” by Karl Popper
- This book covers Popper’s famous philosophy of falsifiability, a cornerstone in understanding scientific reasoning.
- “Bad Science” by Ben Goldacre
- Offers a sharp critique of common misunderstandings and abuses of science, from the media to alternative medicine.
- “Mistakes Were Made (But Not by Me)” by Carol Tavris and Elliot Aronson
- Examines cognitive dissonance, self-justification, and how errors in thinking are reinforced.
3. Cognitive Bias and Fallacies
- “You Are Not So Smart” by David McRaney
- Provides an accessible guide to common cognitive biases and logical fallacies.
- “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli
- A catalog of 99 cognitive biases that affect everyday decision-making and critical thinking.
- “Superforecasting: The Art and Science of Prediction” by Philip Tetlock and Dan M. Gardner
- A deep dive into what makes some people better at predicting future events and how critical thinking is essential in forecasting.
II. Podcasts
1. Critical Thinking and Philosophy
- “Rationally Speaking”
- Discusses critical thinking, philosophy, science, and rationality with guest philosophers, scientists, and thinkers.
- “The Skeptics’ Guide to the Universe”
- A podcast focused on scientific skepticism, debunking myths, and exploring scientific discoveries.
- “The Critical Thinker Podcast”
- Provides bite-sized insights on developing better thinking habits and avoiding cognitive biases.
2. Science and Inquiry
- “Science Vs”
- This podcast tackles popular trends and opinions, pitting them against scientific evidence.
- “Freakonomics Radio”
- Examines the hidden side of things, using economic theory and critical analysis to uncover surprising truths.
- “The Infinite Monkey Cage”
- A witty and accessible podcast that discusses the wonders of science while encouraging critical inquiry.
3. Psychology and Cognitive Bias
- “You Are Not So Smart”
- A companion podcast to the book, exploring cognitive biases, logical fallacies, and why people believe weird things.
- “Hidden Brain”
- Hosted by Shankar Vedantam, this podcast delves into the unconscious patterns driving human behavior and decision-making.
III. Websites and Online Resources
1. Philosophy and Critical Thinking
- Philosophy Now (https://philosophynow.org)
- A magazine that covers contemporary philosophy, engaging readers with critical questions about logic, ethics, and reason.
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (https://plato.stanford.edu)
- A free, scholarly resource that offers in-depth articles on a wide range of philosophical concepts, thinkers, and theories.
- Critical Thinking Web (https://philosophy.hku.hk/think/)
- A comprehensive guide to logic, argument analysis, cognitive biases, and critical thinking techniques.
2. Scientific Skepticism and Inquiry
- Skeptoid (https://skeptoid.com)
- A website and podcast that critically examines myths, urban legends, and pseudoscientific claims.
- Quackwatch (https://quackwatch.org)
- A resource that investigates questionable medical practices and promotes critical evaluation of health claims.
- The Center for Applied Rationality (https://rationality.org)
- Focuses on improving reasoning, decision-making, and overcoming cognitive biases through applied rationality.
3. Cognitive Bias and Fallacies
- Your Logical Fallacy Is (https://yourlogicalfallacyis.com)
- A visually engaging site that explains common logical fallacies and how to avoid them.
- LessWrong (https://lesswrong.com)
- A community blog that explores rationality, biases, and how to improve reasoning in all aspects of life.
IV. Courses and Lectures
1. Free Online Courses
- Critical Thinking at Harvard Extension School (https://online-learning.harvard.edu)
- Offers an introduction to critical thinking through philosophical and real-world problems.
- Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking (Coursera)
- A foundational course on argument analysis, logic, and critical thinking from Duke University.
- Critical Thinking in Global Challenges (Coursera)
- This course examines how critical thinking can address global issues and challenges.
2. Notable Lectures
- “The Art of Critical Decision Making” (The Great Courses)
- A 24-lecture series that offers deep insights into how to improve decision-making through critical thinking strategies.
- Open Yale Courses: Philosophy and the Science of Human Nature (https://oyc.yale.edu/philosophy)
- Free lectures that combine philosophy, cognitive science, and evolutionary psychology to examine human nature.
V. Discussion Forums and Communities
1. Reddit Critical Thinking Subreddits
- r/CriticalThinking: A subreddit dedicated to improving critical thinking and logical reasoning through community discussions and resources.
- r/Philosophy: A large and active community discussing philosophical issues that require in-depth critical thinking.
2. Online Debating Communities
- Kialo (https://www.kialo.com)
- A structured debate platform that encourages clear argumentation and critical evaluation of opposing views.
VI. Practical Exercises and Daily Habits
1. Critical Thinking Apps
- Brilliant (https://brilliant.org)
- Offers daily problem-solving exercises in math, science, and logic that develop critical thinking skills.
- Elevate (https://www.elevateapp.com)
- A brain-training app that includes exercises to improve critical thinking, processing speed, and comprehension.
2. Daily Habits for Critical Thinking
- Practice Socratic Questioning: Make it a daily habit to question assumptions and challenge conclusions, whether reading an article, engaging in conversation, or watching a news report.
- Engage in Debates: Participate in formal or informal debates on controversial or complex topics, requiring you to defend your views logically.
- Write Analytical Essays: Regularly write essays or blog posts analyzing different topics critically, whether current events, ethical dilemmas, or scientific discoveries.
Conclusion
A regular diet of critical thinking content should be well-rounded, with a mix of philosophical, scientific, and practical material. Combining books, podcasts, websites, and interactive exercises ensures that one remains engaged with diverse modes of thought, allowing critical thinking to become a daily habit. By continuously exposing yourself to new ideas and methods of reasoning, you’ll sharpen your analytical abilities and improve your decision-making processes across all areas of life.
Quiz
#1: What is a positive feedback loop between critical thinking and a discipline?
Answer:
A positive feedback loop between critical thinking and a discipline occurs when improvements in one area enhance the other. For example, critical thinking helps to advance scientific research, while scientific challenges further develop critical thinking skills.#2: Name two books that focus on cognitive bias and fallacies mentioned in the framework.
Answer:
“You Are Not So Smart” by David McRaney and “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli.#3: In the framework, what is an example of a podcast focused on science and inquiry?
Answer:
“Science Vs” is an example of a podcast focused on science and inquiry.#4: What type of content does the “Skeptoid” website provide?
Answer:
“Skeptoid” provides critical examinations of myths, urban legends, and pseudoscientific claims.#5: How does critical thinking enhance problem-solving in engineering?
Answer:
Critical thinking allows engineers to question conventional practices, evaluate materials, and design solutions that are innovative and sustainable.#6: What is a key feature of “Philosophy Now” as a resource in the critical thinking framework?
Answer:
“Philosophy Now” is a magazine that covers contemporary philosophy, asking critical questions about logic, ethics, and reason.#7: What daily habit does the framework suggest to improve critical thinking?
Answer:
The framework suggests practicing Socratic questioning daily to challenge assumptions and conclusions in conversations, articles, and news reports.#8: Which cognitive bias is commonly addressed by “The Skeptics’ Guide to the Universe” podcast?
Answer:
“The Skeptics’ Guide to the Universe” podcast often addresses cognitive biases that lead to belief in myths and pseudoscience.#9: Name one online debating platform mentioned in the framework.
Answer:
Kialo is an online debating platform mentioned in the framework.#10: How does engaging with literature help develop critical thinking?
Answer:
Engaging with literature helps develop critical thinking by encouraging readers to interpret complex narratives, analyze themes, and evaluate the author’s intent critically.Provide 20 discussion questions relevant to the content above.
Here are 20 discussion questions that delve into the topics covered:
- How does the ability to critically analyze information differ between the sciences and the humanities? Can these approaches complement each other?
- In what ways can critical thinking lead to innovation in engineering and technology? Provide specific examples.
- How can the medical field benefit from fostering more critical thinking in diagnosis and treatment planning?
- How do cognitive biases hinder critical thinking, and what strategies can be used to mitigate them?
- Discuss the role of critical thinking in ethical decision-making within emerging technologies like AI. What challenges might arise?
- Why is questioning assumptions crucial in both scientific and business decision-making? How can this practice prevent errors?
- In the context of environmental policy, how can critical thinking be used to balance short-term economic interests with long-term ecological sustainability?
- How does critical thinking help historians challenge and reinterpret traditional historical narratives?
- What are the potential dangers of failing to apply critical thinking in evaluating sources of news and information? How does this affect public discourse?
- How does critical thinking aid in dissecting complex legal cases, and what role does it play in the justice system?
- How does exposure to philosophical inquiry improve a person’s ability to engage in critical thinking in everyday life?
- How can engaging with literature or art help develop critical thinking skills? Provide examples from famous works of literature or art that challenge conventional thinking.
- Discuss how critical thinking can enhance personal decision-making in everyday life. Can it be applied in simple daily tasks?
- What role does critical thinking play in scientific hypothesis formation and testing? Why is it crucial for scientific advancement?
- How can debates serve as effective tools to develop and strengthen critical thinking skills? What are the potential pitfalls of debate if critical thinking is not applied?
- How does the concept of a positive feedback loop between critical thinking and various disciplines manifest in education systems? Should critical thinking be taught explicitly in schools?
- In what ways can engaging with different cultures and worldviews improve an individual’s critical thinking abilities?
- What challenges do professionals in business face when critical thinking is overlooked in strategic planning? Can you think of any famous business failures caused by a lack of critical thinking?
- How does critical thinking help in recognizing and addressing common logical fallacies in public or political discourse?
- How can online communities or debate platforms, like Kialo, foster the development of critical thinking in users? Are there any downsides to engaging in such platforms?
These questions are designed to promote deeper thought and discussion on the importance of critical thinking across various disciplines and everyday situations.
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Describe the positive feedback loops between critical thinking and other domains of inquiry.
- Provide ten scenarios that demonstrate the synergistic relationship between critical thinking and other disciplines.
- Create a graph that quantitatively shows the degree of utility of critical thinking in various disciplines.
- Provide a framework for a regular diet of critical thinking content.
- Quiz
- Provide 20 discussion questions relevant to the content above.







Leave a comment