

- Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification, storage, and communication of information.
- Entropy is a measure of uncertainty or randomness in a system.
- Redundancy refers to the repetition of information within a dataset, which can be used to detect and correct errors during data transmission.
- Data Compression is the process of reducing the size of a data file.
- Channel Capacity is the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a communication channel without error.
- Error Detection and Correction techniques like parity checks, checksums, and error-correcting codes are used to detect and correct errors in data transmission.
- Shannon’s 1948 Paper “A Mathematical Theory of Communication” laid the groundwork for information theory, introducing key concepts like entropy and channel capacity.
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Provide an in-depth description of information theory.
- Create a table showing the fields in which information theory is essential, explain its importance to the field, and indicate the degree of future importance to the field.
- Information Theory’s Impact Across Fields
- Provide a list of promising research projects in information theory.
- Let’s focus on how information theory is used in exploring social networks. Write a short, informative essay on this.
- Quizzes
- Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.



Provide an in-depth description of information theory.
Information Theory: An In-Depth Description
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification, storage, and communication of information. Developed by Claude Shannon in the late 1940s, it forms the basis for modern telecommunications, data compression, and data transmission. Here’s a detailed exploration of its core concepts and applications.
Fundamental Concepts
1. Information:
- Information is the resolution of uncertainty. The more uncertain or random an event is, the more information its outcome provides when revealed.
- Information is typically measured in bits. A single bit represents a binary choice (yes/no, on/off).
2. Entropy:
- Entropy is a measure of uncertainty or randomness in a system. In information theory, it quantifies the average amount of information produced by a stochastic source of data.
- Shannon entropy (H) is defined as:
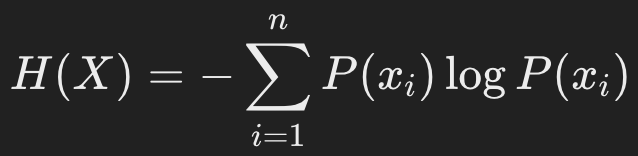 where
where  is the probability of occurrence of the event xix_ixi.
is the probability of occurrence of the event xix_ixi.
3. Redundancy:
- Redundancy refers to the repetition of information within a dataset, which can be used to detect and correct errors during data transmission.
4. Data Compression:
- This is the process of reducing the size of a data file. It can be lossless (no data lost) or lossy (some data lost, typically insignificant to the user).
5. Channel Capacity:
- The maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a communication channel without error.
- Shannon’s Channel Capacity Theorem states:
 where C is the channel capacity, B is the bandwidth, SSS is the signal power, and N is the noise power.
where C is the channel capacity, B is the bandwidth, SSS is the signal power, and N is the noise power.
6. Error Detection and Correction:
- Techniques like parity checks, checksums, and error-correcting codes (e.g., Hamming codes) are used to detect and correct errors in data transmission.
Applications
1. Telecommunications:
- Information theory underpins the operation of modern telecommunication systems, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission.
2. Data Compression:
- Algorithms such as Huffman coding, Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) compression, and JPEG for images use principles of information theory to reduce file sizes.
3. Cryptography:
- Information theory provides a foundation for cryptographic methods, ensuring data security and privacy.
4. Network Information Theory:
- This field extends classical information theory to networks of communication channels, optimizing the flow of information in complex networks like the internet.
5. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence:
- Concepts like entropy and mutual information are used in algorithms for feature selection, classification, and clustering in machine learning.
Key Historical Developments
1. Claude Shannon’s 1948 Paper:
- Shannon’s seminal paper “A Mathematical Theory of Communication” laid the groundwork for information theory, introducing key concepts like entropy and channel capacity.
2. Noisy-Channel Coding Theorem:
- This theorem states that reliable communication is possible over a noisy channel up to a certain maximum rate (the channel capacity).
3. Source Coding Theorem:
- This theorem formalizes the limits of data compression, stating that the average length of the shortest possible representation of the source’s output approaches the entropy of the source.
Practical Examples
1. Compression Algorithms:
- ZIP files use lossless compression algorithms to reduce file size without losing data.
- MP3 and JPEG use lossy compression algorithms to significantly reduce file sizes for audio and images, respectively, by removing data that is less perceptible to humans.
2. Error-Correcting Codes:
- Reed-Solomon codes are used in CDs, DVDs, and QR codes to detect and correct errors.
- Hamming codes are used in computer memory systems to ensure data integrity.
Conclusion
Information theory is a critical field that has transformed the way we store, process, and transmit data. Its principles are foundational to many modern technologies, from telecommunications to machine learning. By understanding and applying these principles, we can optimize and secure the flow of information in various applications.
Delving into Information Theory: The Math of Information
Information theory is a fascinating branch of applied mathematics that deals with the quantification, storage, and transmission of information. It provides a powerful framework for understanding the fundamental limitations and possibilities inherent in communication systems. Pioneered by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, information theory has revolutionized fields like computer science, engineering, and even biology.
Here’s a deeper look at its core concepts:
- The Birth of Information Theory: The groundwork for information theory was laid by Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley in the 1920s. However, Claude Shannon’s groundbreaking 1948 paper, “A Mathematical Theory of Communication,” truly established the field. Shannon’s work provided a mathematical foundation for analyzing communication systems and introduced the concept of entropy, a cornerstone of information theory.
- Entropy: The Measure of Uncertainty: Imagine flipping a coin. There’s a 50% chance of heads or tails, so the uncertainty about the outcome is high. Entropy quantifies this uncertainty. It’s a mathematical measure of the randomness or unpredictability associated with a random variable. High entropy signifies high uncertainty (like the coin toss), while low entropy indicates a predictable outcome (like knowing the sun will rise tomorrow).
- Information as Reducing Uncertainty: When you receive information, you’re essentially reducing uncertainty. Learning the result of the coin toss resolves the initial uncertainty. Information theory deals with how efficiently information can be transmitted to minimize uncertainty at the receiving end.
- Channel Capacity: How Much Information Can You Send?: Imagine a noisy phone line. The information sent (your voice) gets corrupted by noise. Information theory introduces the concept of channel capacity. This is the maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted through a communication channel. Shannon’s channel coding theorem proves that with proper coding techniques, we can approach the channel capacity and transmit information almost error-free, even in the presence of noise.
- Applications of Information Theory: Information theory has a wide range of applications. It’s fundamental to designing efficient data compression algorithms, like those used in ZIP files and image compression. Error-correcting codes used in CDs, DVDs, and even deep-space communication are based on information theory principles. Information theory also plays a role in cryptography, where it helps quantify the security of encryption algorithms.
- Beyond Communication: The concepts of information theory have even found applications in other scientific fields. For instance, in biology, it’s used to study the information content of DNA sequences and the efficiency of information processing in biological systems.
Here are some resources for further exploration:
- Claude Shannon’s paper: A Mathematical Theory of Communication (scholarly resource)
- Khan Academy article on Information Theory: https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/informationtheory
- Stanford University Introduction to Information Theory: http://web.stanford.edu/class/ee276/
Information theory is a rich and constantly evolving field. By understanding its core concepts, you gain valuable insights into how information shapes our world, from sending a text message to unraveling the mysteries of DNA.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the average information content or uncertainty associated with a random variable or a probability distribution. It quantifies the amount of information required to describe a random event or the unpredictability of a data source. Entropy is a central concept in information theory and plays a crucial role in various applications, such as data compression and coding.
Source Coding Theorem
The Source Coding Theorem, also known as the Noiseless Coding Theorem, establishes the fundamental limit on the achievable compression of data. It states that the minimum average number of bits per symbol required to encode a message from a given source (with a known probability distribution) is equal to the entropy of the source. This theorem provides the theoretical basis for lossless data compression algorithms, such as Huffman coding and arithmetic coding.
Channel Capacity
Channel Capacity is a measure of the maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. It is defined as the maximum mutual information between the input and output of the channel, considering the channel’s characteristics and noise. The Channel Coding Theorem, also known as the Noisy Channel Coding Theorem, states that reliable communication is possible over a noisy channel if and only if the information rate is below the channel capacity.
Mutual Information
Mutual Information is a measure of the amount of information that one random variable contains about another random variable. It quantifies the reduction in uncertainty about one variable due to the knowledge of the other variable. Mutual information plays a crucial role in understanding the relationship between random variables and is used in various applications, such as feature selection in machine learning and image registration.
Data Compression
Information theory provides the theoretical foundation for data compression techniques. Lossless compression algorithms, such as Huffman coding and arithmetic coding, aim to compress data without losing any information, exploiting the redundancy in the data source. Lossy compression algorithms, like those used in image and video coding (e.g., JPEG, MPEG), trade off some information for higher compression ratios by introducing controlled distortion.
Error-Correcting Codes
Information theory also underpins the development of error-correcting codes, which are used to detect and correct errors that occur during data transmission or storage. These codes introduce redundancy into the data, enabling the detection and correction of errors within certain limits. Examples include linear block codes, convolutional codes, and turbo codes, which are widely used in communication systems and data storage devices.
Information Theory in Machine Learning
Information theory has found applications in machine learning, particularly in areas such as feature selection, clustering, and information-theoretic learning. Concepts like mutual information and entropy are used to quantify the relevance of features, measure the similarity between data points, and design learning algorithms that optimize information-theoretic criteria.
Create a table showing the fields in which information theory is essential, explain its importance to the field, and indicate the degree of future importance to the field.
Table: Fields in Which Information Theory is Essential
| Field | Explanation of Importance | Degree of Future Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Ensures efficient, reliable data transmission and forms the basis for modern telecommunication systems. | Very High |
| Data Compression | Enables reduction of file sizes, leading to more efficient storage and transmission of data. | Very High |
| Cryptography | Provides foundational concepts for securing data and ensuring privacy through encryption and decryption methods. | Very High |
| Network Information Theory | Optimizes information flow in complex networks, such as the internet, enhancing data transmission efficiency. | High |
| Machine Learning and AI | Utilizes concepts like entropy and mutual information for feature selection, classification, and clustering. | Very High |
| Coding Theory | Develops error-detecting and error-correcting codes to ensure data integrity in transmission and storage. | Very High |
| Quantum Computing | Applies information theory principles to understand and optimize quantum communication and computation processes. | High |
| Bioinformatics | Uses information theory to analyze and interpret biological data, aiding in genome sequencing and protein folding. | Medium |
| Neuroscience | Helps in understanding brain functions and neural networks by analyzing information processing in the brain. | High |
| Economics | Models information flow in markets, aiding in the analysis of economic behaviors and decision-making processes. | Medium |
| Cognitive Science | Studies how humans process information, contributing to the understanding of perception, memory, and learning. | High |
| Linguistics | Analyzes language structure and information transfer, aiding in the development of better communication models. | Medium |
This table summarizes the essential role of information theory across various fields, highlighting its current and future significance in advancing technology, security, data analysis, and understanding complex systems.
Information Theory’s Impact Across Fields
| Field | Importance of Information Theory | Future Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Computer Science | * Data Compression: Lossless compression (ZIP files) and lossy compression (image/video) rely on information theory for optimal data packing. * Error Detection and Correction: Information theory helps design error-correcting codes used in CDs, DVDs, and data transmission for reliable data transfer. * Cryptography: Quantifies the security of encryption algorithms by analyzing information leakage. | High Importance: As data volumes grow, efficient compression and error correction remain crucial. Cryptographic needs will evolve alongside information theory. |
| Electrical Engineering | * Communication Systems Design: Information theory guides the design of communication channels with optimal capacity and noise reduction techniques. * Signal Processing: Helps understand the information content of signals and design efficient processing algorithms. | High Importance: Future communication systems will demand higher bandwidths and information density, making information theory even more critical. |
| Statistics and Machine Learning | * Data Analysis: Information theory concepts like entropy and mutual information help identify patterns and relationships in large datasets. * Model Selection: Information theory can be used to assess the complexity of machine learning models and prevent overfitting. | Increasing Importance: As data analysis becomes more complex, information theory will provide valuable tools for extracting meaning from data. |
| Bioinformatics | * DNA and Protein Sequence Analysis: Information theory helps quantify the information content of genetic sequences and identify functional regions. * Understanding Biological Systems: Information theory can be used to model information processing in biological systems like gene regulation. | Growing Importance: Personalized medicine and advancements in genomics will rely heavily on information theory for data analysis and interpretation. |
Note: This table showcases some key fields. Information theory has applications in other areas like physics, economics, and linguistics as well.
Here’s a table showing the fields where information theory is essential, explaining its importance to the field, and indicating the degree of future importance:
| Field | Importance of Information Theory | Degree of Future Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Communications Engineering | Essential for designing efficient and reliable communication systems, data transmission, and error correction techniques. Provides theoretical foundations for source coding, channel coding, and modulation schemes. | Extremely High – With the ever-increasing demand for high-speed, secure, and reliable communication systems, information theory will continue to play a crucial role in advancing technologies like 5G, 6G, and beyond. |
| Data Compression | Provides the theoretical limits and algorithms for lossless and lossy data compression, enabling efficient storage and transmission of data. Underpins popular compression techniques like Huffman coding, arithmetic coding, and transform coding (e.g., JPEG, MPEG). | High – As the amount of data generated continues to grow exponentially, efficient data compression techniques based on information theory will be invaluable for managing and transmitting large volumes of data. |
| Cryptography and Security | Information theory concepts like entropy and mutual information are used to measure the security and unpredictability of cryptographic systems. Provides theoretical foundations for secure key distribution and encryption algorithms. | High – With the increasing importance of cybersecurity and the need for robust encryption systems, information theory will play a crucial role in developing secure communication and data protection methods. |
| Machine Learning and AI | Information-theoretic measures like entropy and mutual information are used for feature selection, clustering, and designing learning algorithms that optimize information-theoretic criteria. Information theory also provides insights into the fundamental limits of learning and inference. | Very High – As machine learning and AI continue to advance, information theory will be essential for developing more efficient and robust learning algorithms, understanding the limits of learning systems, and analyzing complex data distributions. |
| Biology and Neuroscience | Information theory concepts like entropy and mutual information are used to analyze and understand the behavior of biological systems, gene regulation, and neural coding. Provides a framework for quantifying the information flow in biological processes. | High – With the growing interest in computational biology and the need to analyze large-scale biological data, information theory will be increasingly important for modeling and understanding complex biological systems. |
| Physics and Statistical Mechanics | Entropy plays a fundamental role in statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, and the study of complex systems. Information theory provides a framework for understanding the behavior of physical systems and their information processing capabilities. | Moderate to High – As physicists continue to explore complex systems, quantum computing, and the fundamental limits of information processing, information theory will remain an invaluable tool for understanding and modeling physical phenomena. |
| Economics and Finance | Information theory concepts like entropy and mutual information are used to analyze and model economic systems, financial markets, and decision-making processes. Provides a framework for quantifying uncertainty and information flow in economic and financial systems. | Moderate – While information theory has found applications in economics and finance, its future importance in these fields may depend on the development of new theoretical frameworks and practical applications. |
It’s important to note that information theory is a highly interdisciplinary field, and its principles and concepts have the potential to find applications in many other domains as well. As technology and scientific understanding continue to advance, the importance of information theory is likely to grow across various fields.
Provide a list of promising research projects in information theory.
Promising Research Projects in Information Theory
1. Quantum Information Theory:
- Objective: Develop theories and methods for efficient quantum communication and computation.
- Impact: Enhance the capabilities of quantum computers and secure quantum communication networks.
2. Machine Learning and Information Theory Integration:
- Objective: Apply information-theoretic concepts to improve machine learning algorithms, such as in feature selection and neural network optimization.
- Impact: Create more efficient and effective AI models, leading to advancements in various AI applications.
3. Network Coding and Information Flow:
- Objective: Develop new coding strategies to optimize information flow in large, complex networks like the internet and IoT.
- Impact: Improve data transmission efficiency and reliability, enhancing the performance of communication networks.
4. Privacy-Preserving Data Compression:
- Objective: Create data compression algorithms that maintain data privacy while reducing file sizes.
- Impact: Protect sensitive information in compressed formats, ensuring security and privacy in data storage and transmission.
5. Bioinformatics and Genomic Data Analysis:
- Objective: Apply information theory to analyze and interpret large-scale genomic data, focusing on sequence alignment and gene expression analysis.
- Impact: Advance our understanding of genetic information, leading to breakthroughs in personalized medicine and biotechnology.
6. Information-Theoretic Security:
- Objective: Develop new cryptographic protocols based on information theory to enhance data security against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
- Impact: Ensure robust data protection and privacy in digital communications and transactions.
7. Error-Correcting Codes for Emerging Technologies:
- Objective: Design advanced error-correcting codes tailored for next-generation technologies like 5G, 6G, and space communications.
- Impact: Improve the reliability and efficiency of data transmission in cutting-edge communication systems.
8. Cognitive Neuroscience and Information Processing:
- Objective: Investigate how the brain processes information using information-theoretic models, focusing on perception, memory, and decision-making.
- Impact: Enhance our understanding of brain function and cognitive processes, contributing to advances in neuroscience and artificial intelligence.
9. Information Theory in Social Networks:
- Objective: Analyze the flow of information in social networks to understand influence, misinformation, and the spread of ideas.
- Impact: Develop strategies to mitigate misinformation and enhance the positive impact of information sharing in social networks.
10. Linguistic Information Theory:
- Objective: Study the structure and transmission of information in languages to improve natural language processing and communication models.
- Impact: Improve language technologies, such as translation services and speech recognition systems.
These research projects represent the forefront of information theory, addressing current challenges and exploring new frontiers in technology, security, data analysis, and our understanding of complex systems.
Here are some promising research areas in information theory:
- Quantum Information Theory: This branch explores the application of information theory principles to quantum mechanics. It has the potential to revolutionize communication and computation with advancements in quantum computers and communication channels. Research areas include quantum error correction, quantum cryptography, and developing new information measures for quantum systems.
- Information Theory and Machine Learning: The intersection of these fields is leading to exciting developments. Researchers are exploring how information theory can be used to improve the efficiency and interpretability of machine learning models. This includes using information bottleneck methods for dimensionality reduction and developing information-theoretic bounds for learning performance.
- Network Information Theory: This field focuses on information flow in networks, particularly communication networks. Research areas include reliable communication in unreliable networks, information dissemination in social networks, and efficient routing protocols based on information theory principles.
- Information Theory and High-Dimensional Data: Traditional information theory often struggles with high-dimensional data, common in modern datasets. Researchers are developing new information measures and techniques to analyze and compress such data effectively.
- Information Theory and Complexity: This area explores the connection between information processing and computational complexity. It aims to understand the fundamental limitations on how efficiently information can be processed and manipulated by computers or physical systems.
- The Thermodynamics of Information: This emerging field investigates the relationship between information processing and physical laws like thermodynamics. Research focuses on understanding the energy cost of information processing and storage, with implications for areas like nanocomputing and biological information processing.
These are just a few examples, and the field of information theory is constantly evolving. As technology advances and new challenges emerge, researchers will continue to explore new frontiers in information theory, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in communication, computation, and data analysis.
Promising Research Projects in Information Theory
- Quantum Information Theory
- Exploring the fundamental limits of quantum computing and quantum communication systems
- Developing new quantum error-correction codes and quantum cryptography protocols
- Studying the interplay between quantum mechanics and information theory
- Network Information Theory
- Designing efficient and secure communication protocols for large-scale networks (e.g., Internet of Things, sensor networks)
- Analyzing the capacity and scaling laws of complex networks
- Developing distributed source and channel coding techniques for network communications
- Biological Information Theory
- Modeling and understanding the information processing capabilities of biological systems (e.g., gene regulatory networks, neural coding)
- Developing information-theoretic frameworks for analyzing and interpreting biological data (e.g., genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data)
- Exploring the connections between information theory, evolution, and the origin of life
- Machine Learning and Information Theory
- Developing information-theoretic frameworks for analyzing and optimizing machine learning algorithms
- Exploring the fundamental limits of learning and inference from an information-theoretic perspective
- Applying information theory to areas like deep learning, reinforcement learning, and generative models
- Neuroscience and Information Theory
- Quantifying and modeling the information flow in neural systems
- Understanding the principles of neural coding and information processing in the brain
- Developing information-theoretic models for brain-computer interfaces and neuroprosthetics
- Quantum Information and Gravity
- Investigating the connections between quantum information theory and theories of quantum gravity (e.g., black hole information paradox)
- Exploring the role of information in the physics of black holes and the holographic principle
- Information Theory and Cryptography
- Developing new secure communication and encryption protocols based on information-theoretic principles
- Analyzing the information-theoretic limits of cryptographic systems and their security against quantum computing attacks
- Exploring the connections between information theory, randomness, and computational complexity
- Information Theory and Statistical Physics
- Bridging the gap between information theory and statistical mechanics
- Analyzing the information processing capabilities of physical systems and their thermodynamic limits
- Developing information-theoretic frameworks for understanding non-equilibrium processes and emergent phenomena
- Distributed Information Theory
- Designing efficient distributed source and channel coding techniques for decentralized systems
- Analyzing the fundamental limits of distributed computation and information processing
- Exploring applications in areas like distributed machine learning, blockchain, and edge computing
- Information Theory and Complexity
- Investigating the connections between information theory and computational complexity theory
- Analyzing the information complexity of algorithms and computational problems
- Exploring the role of information in understanding the limits of computation and the nature of complexity
These research projects span a wide range of disciplines, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of information theory and its potential to advance our understanding of various scientific and technological fields.
Let’s focus on how information theory is used in exploring social networks. Write a short, informative essay on this.
The Role of Information Theory in Exploring Social Networks
Introduction
Social networks are complex systems where information is continuously generated, shared, and propagated among individuals and groups. Understanding the dynamics of these networks is crucial for various applications, ranging from marketing and public health to political science and sociology. Information theory provides a robust framework to analyze and interpret the flow of information within these networks, offering insights into influence, communication patterns, and the spread of information and misinformation.
Information Flow and Influence
One of the primary applications of information theory in social networks is analyzing how information flows through the network. By quantifying information transmission using metrics such as mutual information and entropy, researchers can identify influential nodes (individuals or groups) that significantly impact the spread of information. These metrics help in understanding which users are central to disseminating information and how effectively they do so.
For instance, in marketing, identifying key influencers can help brands target their campaigns more efficiently. In public health, understanding how information about health practices spreads can assist in designing effective communication strategies to promote healthy behaviors.
Detecting and Mitigating Misinformation
Misinformation and disinformation are significant challenges in social networks. Information theory helps in detecting the spread of false information by analyzing the entropy of information sources and the paths through which information spreads. Higher entropy in the context of information sources might indicate a higher degree of unpredictability and potential misinformation.
Researchers can use these insights to develop algorithms that flag potential misinformation and trace its origins. Additionally, by understanding the pathways through which misinformation spreads, it is possible to design interventions to disrupt these paths and promote accurate information.
Community Detection and Network Structure
Information theory aids in uncovering the underlying structure of social networks by identifying communities within the network. Modularity and mutual information between nodes can be used to detect clusters of users who interact more frequently with each other than with the rest of the network. These clusters often represent communities with shared interests or characteristics.
Understanding these communities is vital for various applications, such as tailoring content to specific user groups or studying the diffusion of innovations within particular segments of the population. It also helps in identifying echo chambers where similar ideas are reinforced while opposing views are excluded, which is crucial for understanding the dynamics of public opinion and polarization.
Viral Information Spread
The concept of information entropy is also used to model and predict the viral spread of information. By analyzing past data on how certain types of content go viral, researchers can develop models that predict the potential virality of new content. These models consider factors such as the initial set of sharers, the content’s novelty, and the network’s structure.
Predicting viral spread has significant implications for various domains, including marketing, where companies can strategically design and launch campaigns to maximize reach. It also helps in public health and safety, where predicting the spread of critical information can ensure timely dissemination to prevent crises.
Conclusion
Information theory offers powerful tools for analyzing and interpreting the complexities of social networks. By quantifying information flow, detecting misinformation, understanding network structure, and predicting viral spread, researchers and practitioners can harness these insights to improve communication strategies, design effective interventions, and foster healthier information ecosystems. As social networks continue to evolve and grow, the role of information theory in exploring these networks will become increasingly vital, driving innovation and enhancing our understanding of these intricate systems.
Unveiling the Social Web: How Information Theory Illuminates Social Networks
Social networks, the digital landscapes where we connect and share, have become an intricate part of our lives. But beneath the surface of likes and comments lies a complex flow of information. Information theory, with its focus on quantifying information, sheds light on how information travels and shapes our interactions within these networks.
One key concept, entropy, helps us understand the diversity of information flow. A network with high entropy, where users share a wide variety of content, presents a rich information landscape. Conversely, low entropy networks, with repetitive or homogenous content, offer less information variety. By analyzing entropy, researchers can identify communities within a network that share similar information patterns.
Information theory also helps us grasp how information cascades through a network. The concept of mutual information, which measures the shared information between two nodes (users), allows researchers to identify influential users who drive information diffusion. Understanding these dynamics helps predict how trends and ideas spread within a network.
Furthermore, information theory paves the way for the development of efficient algorithms for network analysis. By quantifying the information content of connections and interactions, researchers can design algorithms to identify key players, detect communities, and even predict future connections within the network.
However, applying information theory to social networks presents challenges. Social data is often noisy and subjective. Moreover, user behavior can be unpredictable, making it difficult to model information flow with perfect accuracy.
Despite these challenges, information theory offers a powerful lens for understanding social networks. It equips researchers with tools to measure information diversity, identify influential users, and predict information spread. As social networks continue to evolve, information theory will remain a valuable tool for navigating the ever-growing web of our social interactions.
Information Theory and Social Networks: Unveiling the Dynamics of Information Flow
In the era of digital connectivity, social networks have become ubiquitous, shaping the way we interact, communicate, and exchange information. These complex webs of relationships and interactions have attracted significant interest from researchers across various disciplines, including information theory. By employing the principles and tools of information theory, scientists are uncovering valuable insights into the dynamics of information flow within social networks, paving the way for a deeper understanding of human behavior and social phenomena.
Quantifying Information Flow
At the heart of applying information theory to social networks lies the concept of entropy. Entropy, a fundamental measure of uncertainty or information content, provides a quantitative means to analyze the flow of information within a network. By treating individuals as nodes and their interactions as edges, researchers can model social networks as complex systems and investigate how information propagates through these intricate structures.
One key area of interest is the study of information diffusion, which examines how ideas, rumors, or trends spread across a network. Information theory offers powerful tools, such as mutual information and transfer entropy, to quantify the extent to which one node’s state or behavior is influenced by another node’s information. This analysis can shed light on the mechanisms driving the viral spread of information, as well as identify influential nodes or communities that play pivotal roles in the dissemination process.
Network Structure and Dynamics
Information theory also provides valuable insights into the structural properties of social networks. By analyzing the entropy and mutual information between nodes, researchers can uncover the underlying patterns and dependencies within the network. This knowledge can be leveraged to identify communities, detect bottlenecks in information flow, and understand the resilience and robustness of the network to perturbations or attacks.
Moreover, information theory offers a framework for studying the temporal dynamics of social networks. Concepts like transfer entropy and information transfer maps can be employed to analyze the directional flow of information between nodes over time. This approach has applications in areas such as rumor detection, influence analysis, and understanding the evolution of social trends and behaviors.
Applications and Implications
The applications of information theory in social network analysis span various domains, including marketing, public health, and national security. For instance, in marketing, understanding information diffusion patterns can aid in designing effective viral marketing campaigns or identifying influential individuals for targeted advertising. In public health, analyzing information flow can help track the spread of misinformation or monitor the dissemination of health-related messages, enabling more effective intervention strategies.
Furthermore, the insights gained from information-theoretic analyses of social networks have implications for privacy and security. By understanding the flow of information within a network, researchers can identify potential vulnerabilities or privacy risks, leading to the development of more robust privacy-preserving mechanisms and security protocols.
As social networks continue to shape our digital landscape, the application of information theory offers a powerful lens through which to unravel the intricate dynamics of information flow and human behavior. By leveraging the quantitative rigor of information theory, researchers can unlock valuable insights, paving the way for more effective communication strategies, better understanding of social phenomena, and innovative solutions to complex challenges in our interconnected world.
Quizzes
#1: Who is considered the founder of Information Theory?
Answer:
Claude Shannon
#2: What is entropy in the context of Information Theory?
Answer:
Entropy is a measure of uncertainty or randomness in a system, quantifying the average amount of information produced by a stochastic source of data.
#3: What is the primary unit of measurement for information in Information Theory?
Answer:
The bit, which represents a binary choice (yes/no, on/off).
#4: Explain the significance of channel capacity in Information Theory.
Answer:
Channel capacity is the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a communication channel without error.
#5: Name two fields where Information Theory is essential and explain its importance in each.
Answer:
Telecommunications: Ensures efficient, reliable data transmission and forms the basis for modern telecommunication systems.
Cryptography: Provides foundational concepts for securing data and ensuring privacy through encryption and decryption methods.
#6: How does Information Theory help in detecting misinformation in social networks?
Answer:
By analyzing the entropy of information sources and the paths through which information spreads, higher entropy may indicate potential misinformation.
#7: Describe the concept of redundancy in Information Theory.
Answer:
Redundancy refers to the repetition of information within a dataset, which can be used to detect and correct errors during data transmission.
#8: What role does Information Theory play in bioinformatics?
Answer:
Information Theory is used to analyze and interpret large-scale genomic data, aiding in sequence alignment and gene expression analysis.
#9: What is the significance of mutual information in the context of social networks?
Answer:
Mutual information helps identify influential nodes in a network by quantifying the amount of information shared between nodes.
#10: How can Information Theory improve machine learning algorithms?
Answer:
By applying concepts like entropy and mutual information for feature selection, classification, and clustering, leading to more efficient and effective AI models.
1: What is the field of study concerned with quantifying, storing, and transmitting information?
Answer:
Information theory
2: Who is credited with pioneering information theory in the 1940s?
Answer:
Claude Shannon
3: What is the measure of randomness or unpredictability associated with a random variable in information theory?
Answer:
Entropy
4: According to information theory, what does receiving information essentially do?
Answer:
Reduce uncertainty
5: What is the maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted through a communication channel?
Answer:
Channel capacity
6: In which field is information theory used to design efficient data compression algorithms like ZIP files?
Answer:
Computer Science
7: What concept in information theory helps identify communities within a social network that share similar information patterns?
Answer:
Entropy
8: What is the measure of shared information between two nodes (users) in a network?
Answer:
Mutual information
9: What emerging area of research explores the connection between information processing and physical laws like thermodynamics?
Answer:
The Thermodynamics of Information
10: What is a challenge in applying information theory to social networks?
Answer:
Social data can be noisy and subjective, and user behavior can be unpredictable.
#1: What is the central concept in information theory that quantifies the amount of information required to describe a random event or the unpredictability of a data source?
Answer:
Entropy
#2: What theorem establishes the fundamental limit on the achievable compression of data?
Answer:
The Source Coding Theorem (or Noiseless Coding Theorem)
#3: What is the measure of the maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel?
Answer:
Channel Capacity
#4: What is the term used to describe the amount of information that one random variable contains about another random variable?
Answer:
Mutual Information
#5: Which field is exploring the connections between information theory and theories of quantum gravity, such as the black hole information paradox?
Answer:
Quantum Information and Gravity
#6: What concept from information theory is used to quantify the extent to which one node’s state or behavior is influenced by another node’s information in a social network?
Answer:
Mutual Information and Transfer Entropy
#7: What information theory concept provides a quantitative means to analyze the flow of information within a network?
Answer:
Entropy
#8: Which field is exploring the development of new secure communication and encryption protocols based on information-theoretic principles?
Answer:
Information Theory and Cryptography
#9: What concept from information theory is used to analyze the information processing capabilities of physical systems and their thermodynamic limits?
Answer:
Entropy
#10: Which area of research is investigating the connections between information theory and computational complexity theory, analyzing the information complexity of algorithms and computational problems?
Answer:
Information Theory and Complexity
Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.
Discussion Questions on Information Theory
- What are the key contributions of Claude Shannon to Information Theory, and how have they influenced modern telecommunications?
- How does the concept of entropy in Information Theory differ from its usage in thermodynamics, and what are the implications of these differences?
- In what ways can data compression techniques be improved by leveraging advancements in Information Theory?
- Discuss the role of redundancy in error detection and correction. How does it impact the efficiency of data transmission?
- How can Information Theory be applied to enhance the security of cryptographic systems against evolving cyber threats?
- What are the challenges and potential solutions in optimizing information flow in large, complex networks like the Internet of Things (IoT)?
- How do concepts from Information Theory integrate with machine learning to improve model performance and data analysis? Provide examples.
- Examine the impact of quantum Information Theory on the future of computing and communication. What are the key areas of research in this field?
- Discuss the importance of Information Theory in bioinformatics, particularly in genomic data analysis. What are some recent advancements in this area?
- In what ways can Information Theory aid in understanding brain function and cognitive processes in neuroscience?
- Analyze the role of Information Theory in social networks. How can it help in identifying influential users and understanding information dissemination?
- How does the use of mutual information contribute to community detection within social networks, and what are the practical applications of this knowledge?
- What are the ethical considerations involved in using Information Theory for social network analysis, particularly concerning privacy and data security?
- Discuss the potential of Information Theory in mitigating the spread of misinformation in social networks. What strategies can be implemented based on this approach?
- How can future research in Information Theory contribute to advancements in artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies? What are the promising areas of exploration?
These questions are designed to encourage deep thinking and discussion about the various aspects and applications of Information Theory, promoting a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Beyond bits and bytes, how can information theory be used to quantify the “meaning” or “importance” of information?
- Imagine a social media platform focused entirely on sharing images. How would information theory be applied differently compared to a platform with text and video content?
- Could information theory be used to combat the spread of misinformation in social networks? If so, how?
- With the rise of personalized news feeds and social media bubbles, how can information theory help us understand the potential for echo chambers and filter bubbles?
- Can information theory be used to predict the virality of online content, or is it too dependent on unpredictable user behavior?
- How might advancements in quantum information theory impact the way information flows and is secured within social networks?
- In the context of social networks, how can we differentiate between healthy information diversity and information overload?
- Does information theory have ethical implications when applied to social networks? Could it be used for manipulative purposes?
- How can the concept of channel capacity be applied to understand the limitations of human information processing in social media environments?
- Beyond social networks, what other areas of human communication could benefit from applying information theory principles?
- As artificial intelligence becomes more integrated with social networks, how can information theory be used to ensure responsible and unbiased information flow?
- Can information theory help us understand the evolution of online language and communication patterns within social media platforms?
- How can we leverage information theory to design social media algorithms that promote meaningful interactions and reduce the spread of negativity?
- With the increasing decentralization of online communication, how can information theory principles be adapted to analyze information flow in a more distributed network structure?
- Information theory focuses on quantifiable data. How can we integrate qualitative aspects of human communication, like emotions and cultural context, into information theory frameworks for social networks?
Here are 15 discussion questions relevant to the content on information theory:
- How has the concept of entropy in information theory influenced our understanding of complex systems in fields like physics and biology?
- What are the potential implications of quantum information theory for the development of secure communication systems and quantum computing?
- Discuss the role of information theory in the field of machine learning, and how it can help in understanding the fundamental limits of learning and inference.
- How can the principles of information theory be applied to design efficient and secure communication protocols for large-scale networks, such as the Internet of Things or sensor networks?
- Explore the connections between information theory and cryptography, and how these fields can contribute to the development of robust encryption and security protocols.
- In what ways can information theory be used to analyze and model the behavior of financial markets and economic systems?
- Discuss the potential applications of information theory in the field of neuroscience, particularly in understanding neural coding and information processing in the brain.
- How can the concepts of mutual information and transfer entropy be utilized to study the dynamics of information flow within social networks?
- Explore the role of information theory in the field of computational biology, and how it can aid in the analysis and interpretation of biological data, such as genomic and proteomic data.
- Discuss the potential impact of information theory on our understanding of the physics of black holes and the holographic principle, particularly in the context of the black hole information paradox.
- How can the principles of distributed information theory be applied to design efficient distributed computing systems and algorithms for decentralized environments?
- Explore the connections between information theory and statistical mechanics, and how these fields can inform our understanding of non-equilibrium processes and emergent phenomena.
- Discuss the potential applications of information theory in the field of privacy and security, particularly in identifying vulnerabilities and developing privacy-preserving mechanisms.
- How can the principles of information theory be used to analyze and optimize the performance of error-correcting codes and data compression algorithms?
- Discuss the role of information theory in bridging the gap between different scientific disciplines and facilitating interdisciplinary research collaborations.
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Provide an in-depth description of information theory.
- Create a table showing the fields in which information theory is essential, explain its importance to the field, and indicate the degree of future importance to the field.
- Information Theory’s Impact Across Fields
- Provide a list of promising research projects in information theory.
- Let’s focus on how information theory is used in exploring social networks. Write a short, informative essay on this.
- Quizzes
- Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.






Leave a comment