

- “Conflicts of interest arise when researchers have personal or financial interests that could affect their judgment or the integrity of their research.” This quote points to the bias that can occur in scientific research.
- “If the sample used in a study does not accurately represent the larger population, the findings may not be generalizable.” This quote stresses the importance of representative samples in research.
- “Misinterpreted results occur when media or articles twist or oversimplify the findings of scientific studies.” This underscores the common issue of media misrepresentation.
- “Just because two trends occur together does not mean one causes the other.” This emphasizes the critical distinction between correlation and causation.
- “Studies that have not undergone peer review might lack scrutiny and carry biases not checked by other experts.” This highlights the critical role of peer review in validating scientific findings.
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Elaborate on each of the 12 points in this image.
- Elaborate on the 12 Points on Spotting Bad Science
- 1. Sensationalized Headlines
- 2. Misinterpreted Results
- 3. Conflicts of Interest
- 4. Correlation & Causation
- 5. Unsupported Conclusions
- 6. Problems with Sample Size
- 7. Unrepresentative Samples Used
- 8. No Control Group Used
- 9. No Blind Testing Used
- 10. Selective Reporting of Data
- 11. Unreplicable Results
- 12. Non-Peer Reviewed Material
- Elaborate on the 12 Points on Spotting Bad Science
- Which domains of science are most susceptible to the abandonment of proper science, and what commonly drives its abandonment?
- Provide an extensive list of questions we should ask whenever a scientific claim is made.
- Create a 10-item quiz on the entire thread above.
- Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.



Elaborate on each of the 12 points in this image.
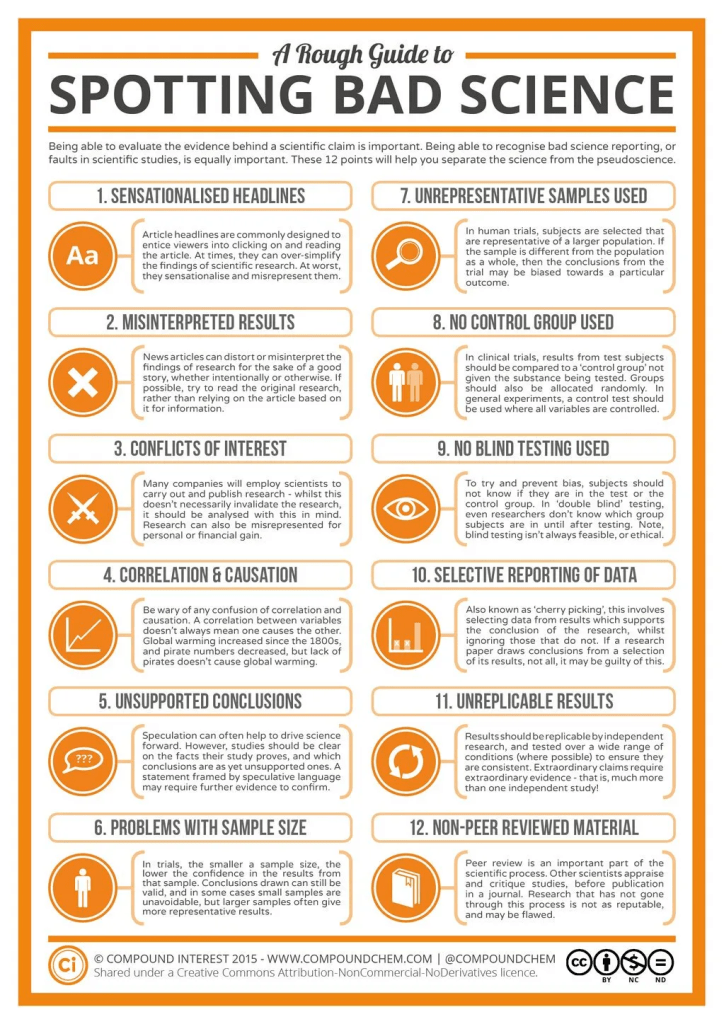
Elaborate on the 12 Points on Spotting Bad Science
1. Sensationalized Headlines
Headlines that are sensationalized are crafted to attract more viewers by exaggerating or distorting the truth. These types of headlines often rely on shock value and may not accurately represent the findings of the research, potentially misleading the reader.
2. Misinterpreted Results
This occurs when media or articles twist or oversimplify the findings of scientific studies. Often, complex results are reduced to eye-catching headlines that fail to convey the limitations or the full context of the research, leading to public misunderstanding.
3. Conflicts of Interest
Conflicts of interest arise when researchers have personal or financial interests that could affect their judgment or the integrity of their research. This can lead to biased results if the study is conducted or presented in a way that favors the researcher’s interests.
4. Correlation & Causation
A common error in science reporting is confusing correlation (a relationship between two variables) with causation (one variable directly influencing another). Just because two trends occur together does not mean one causes the other, and misrepresenting this relationship can lead to faulty conclusions.
5. Unsupported Conclusions
Researchers may sometimes draw conclusions that are not fully supported by their data. This can occur due to over-speculation, lack of data, or pushing a narrative beyond what the evidence can substantiate.
6. Problems with Sample Size
A small sample size can lead to unreliable and non-representative results because the variation in a small group might not reflect the larger population. Larger and more diverse sample sizes tend to provide more reliable and applicable results.
7. Unrepresentative Samples Used
If the sample used in a study does not accurately represent the larger population, the findings may not be generalizable. This skew in sample selection can lead to biased outcomes that do not accurately reflect the broader context.
8. No Control Group Used
Control groups are crucial for comparing outcomes in experiments, particularly in clinical trials. Without a control group, it is difficult to determine whether the results are due to the factor being tested or other external variables.
9. No Blind Testing Used
Blind testing, especially double-blind testing where neither participants nor researchers know who belongs to the control group, helps to prevent bias in scientific studies. Absence of blinding can lead to biases in data collection and analysis.
10. Selective Reporting of Data
This involves cherry-picking data that supports a particular conclusion while ignoring data that does not. Such selective reporting can distort the understanding of a study’s outcomes and mislead stakeholders about the actual findings.
11. Unreplicable Results
Scientific findings should be replicable by independent researchers using the same methodologies. Studies that cannot be replicated are less credible as they may indicate experimental errors, misinterpretations, or fraudulent practices.
12. Non-Peer Reviewed Material
Peer review is a process where other experts in the field evaluate the research before it is published. Studies that have not undergone peer review might lack scrutiny and carry biases not checked by other experts, making them less reliable.
Sure, the image you sent is titled “A Rough Guide to Spotting Bad Science” by Compound Interest. It outlines 12 points to help you evaluate scientific claims and distinguish between real science and pseudoscience. Here’s a breakdown of each point:
- Sensationalized Headlines: Attention-grabbing headlines can be misleading and oversimplify complex scientific findings. They may use unnecessary drama or excitement to draw you in, but not accurately reflect the research.
- Misinterpreted Results: News articles may distort or misunderstand scientific studies, either accidentally or intentionally, to create a more interesting story. It’s important to consult the original research whenever possible.
- Conflicts of Interest: Sometimes, scientists who conduct research have financial or personal ties to the product or industry being studied. This can bias their findings, so it’s important to be aware of any potential conflicts.
- Correlation vs. Causation: Just because two things appear to be related doesn’t necessarily mean one causes the other. This is a common mistake in pseudoscience, and critical thinking is needed to avoid misinterpretations.
- Unsupported Conclusions: Speculation is a part of scientific inquiry, but well-designed studies should focus on the evidence and avoid presenting unsupported theories or conclusions as facts.
- Problems with Sample Size: Studies with very small sample sizes may not be statistically significant, meaning the results may not be generalizable to the entire population. Larger samples tend to provide more reliable results.
- Unrepresentative Samples: If the study group doesn’t accurately reflect the population being studied, the results may be biased and misleading. For instance, a study on a weight loss drug tested only on young, healthy adults might not be applicable to a broader population.
- No Control Group Used: In controlled experiments, a control group that does not receive the treatment or intervention being studied is used as a baseline for comparison. Without a control group, it’s difficult to determine if the treatment caused the observed effects.
- No Blind Testing Used: Ideally, studies should be double-blind, where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is in the treatment or control group. This helps to reduce bias that can influence the results.
- Selective Reporting of Data: Researchers may focus on data that supports their hypothesis and neglect to mention findings that contradict it. This is known as “cherry picking” and can lead to misleading conclusions.
- Unreplicable Results: Credible scientific findings can be replicated by other researchers using similar methods. If a study’s results cannot be replicated, it casts doubt on their validity.
- Non-Peer-Reviewed Material: Peer review is a crucial part of the scientific process. Other scientists review and critique research papers before they are published in reputable scientific journals. Non-peer-reviewed material has not undergone this scrutiny and may be less reliable.
The image provides a helpful guide on identifying 12 potential signs or issues that could indicate bad science or pseudoscience. Let me elaborate on each point:
- Sensationalised Headlines: Scientific findings are often sensationalized in news headlines to attract readers, exaggerating or misrepresenting the actual research conclusions.
- Misinterpreted Results: News articles may distort or misinterpret research findings, either intentionally or unintentionally, providing an inaccurate portrayal instead of relying on the original study.
- Conflicts of Interest: Companies or researchers may have personal or financial interests that could bias their research, so potential conflicts should be considered when evaluating studies.
- Correlation & Causation: The image warns against confusing correlation (a relationship between variables) with causation (one variable directly causing the other), as correlations don’t necessarily imply causation.
- Unsupported Conclusions: While speculation can drive scientific progress, conclusions should be supported by evidence, and speculative language alone may require further confirmation.
- Problems with Sample Size: Small sample sizes in studies can limit the confidence in the results, while larger samples often provide more representative findings.
- Unrepresentative Samples Used: In human trials, the selected subjects should be representative of the larger population to avoid biased outcomes favoring particular groups.
- No Control Group Used: In clinical trials, having a control group that doesn’t receive the treatment is crucial for comparing results and accounting for potential confounding factors.
- No Blind Testing Used: Blind testing, where participants and researchers are unaware of who receives the treatment or placebo, helps prevent biases from influencing the outcomes.
- Selective Reporting of Data: Also known as “cherry-picking,” this involves selectively reporting data that supports a desired conclusion while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Unreplicable Results: Scientific findings should be replicable by independent research and hold true across various conditions, rather than relying on extraordinary, one-time observations.
- Non-Peer Reviewed Material: Peer review, where studies are scrutinized and critiqued by experts before publication, is an essential part of the scientific process, lending credibility to the research.
Overall, this guide highlights important factors to consider when evaluating scientific claims, such as potential biases, methodological flaws, lack of reproducibility, and the credibility of the sources and peer review process.
Which domains of science are most susceptible to the abandonment of proper science, and what commonly drives its abandonment?
Domains of Science Susceptible to Abandoning Proper Science
Certain domains of science may be more susceptible to deviations from proper scientific methods due to various pressures and the nature of the research. Here are some areas particularly vulnerable:
1. Nutritional Science
Nutritional science often faces challenges due to varying individual responses to diet, difficulties in controlling long-term dietary studies, and frequent conflicts of interest with food companies and industries. This can lead to sensationalized findings and frequently changing dietary recommendations.
2. Pharmaceutical Research
Pharmaceutical research can be prone to issues due to the significant financial stakes involved. The desire to develop profitable drugs can lead to conflicts of interest, publication bias (favoring positive results), and in some cases, data manipulation.
3. Psychology
Psychology, particularly fields dealing with complex and variable human behaviors, can struggle with replicating results. The replication crisis, highlighted in recent years, showcases the difficulties in replicating many psychological studies due to factors like small sample sizes and variable experimental designs.
4. Environmental Science
Environmental science can be politicized, especially when research findings have implications for regulations and policies. This can lead to bias, pressure from stakeholders, and selective reporting, particularly in areas like climate change and pollution.
5. Economic Studies
Economic research can be influenced by ideological biases and funding sources, especially when studies could affect policy decisions. Economic models can also be overly simplistic or based on incorrect assumptions, leading to misleading conclusions.
Common Drivers for Abandoning Proper Science
Several factors can drive the abandonment of proper scientific methods across these domains:
Financial Incentives
Financial gain can significantly influence research outcomes. In pharmaceuticals, for example, the potential profits from new drugs can tempt companies to selectively report positive results or rush studies without thorough peer review.
Political and Ideological Pressure
Research that has policy implications may be subject to pressures from political groups or governments, which can lead to biased outcomes or suppression of unfavorable results.
Media Influence
The desire for media attention can lead researchers or institutions to hype preliminary findings or present results in a sensationalized manner, which is particularly common in fields like nutritional science.
Complexity and Methodological Limitations
In fields where variables are difficult to control or measure, such as psychology and environmental science, methodological challenges can lead to inconsistent or non-reproducible results.
These vulnerabilities and pressures highlight the importance of robust peer review processes, transparency in funding and methodology, and ongoing efforts to improve research practices across all domains of science.
It’s important to acknowledge that any scientific field can potentially fall prey to practices that deviate from proper scientific methodology. However, some domains might be more susceptible for various reasons:
Fields with a strong commercial or ideological bent:
- Nutrition Science: The weight loss industry and supplement manufacturers often fund research with a vested interest in promoting specific products. This can lead to biased studies and sensationalized claims.
- Environmental Science: Industries that might be negatively impacted by environmental regulations may sponsor research that downplays the severity of environmental problems. Conversely, some advocacy groups might cherry-pick data to support their cause.
Fields with difficulty in conducting controlled experiments:
- Psychology: Studying human behavior is complex because it’s influenced by many factors. It can be challenging to isolate variables and conduct double-blind experiments, making it easier for biases to creep in.
- Social Sciences: Similar to psychology, studying social phenomena often involves large numbers of people and complex interactions. This makes it difficult to control for all variables and can lead to conflicting research results.
Fields with a large amount of anecdotal evidence:
- Alternative Medicine: Many alternative medicine practices rely heavily on testimonials and personal experiences. Anecdotes are not scientific evidence, and the placebo effect can often account for perceived benefits.
- Parapsychology: The study of paranormal phenomena is inherently difficult to design rigorous experiments for, making it susceptible to confirmation bias and unreliable data collection methods.
Common Drivers of Abandoning Proper Science:
- Financial Gain: As mentioned earlier, the promise of financial rewards can motivate researchers or institutions to prioritize commercial interests over rigorous methodology.
- Ideological Biases: Researchers with strong pre-existing beliefs about a topic might design studies or interpret data in a way that confirms those beliefs, regardless of the actual evidence.
- Pressure to Publish: In academic circles, pressure to publish research can lead to rushing studies through the peer-review process or focusing on sensational results that get noticed, even if the methodology is weak.
- Lack of Scientific Literacy: The general public might struggle to distinguish between credible scientific studies and pseudoscience, making them vulnerable to misinformation and sensationalized claims.
It’s important to remember:
- Even in susceptible fields, there are plenty of reputable scientists conducting high-quality research.
- Critical thinking and information literacy are essential tools for evaluating scientific claims.
- Look for research published in peer-reviewed journals, consider the source of funding, and be wary of sensationalized headlines and unsupported conclusions.
Several domains of science can be susceptible to abandoning proper scientific methods and principles, often driven by certain pressures or motivations. Here are some examples:
- Medical and pharmaceutical research: The profit motivations of drug companies and the potential for financial gain can lead to cutting corners, selective reporting of favorable data, downplaying negative findings, or even fraudulent practices in clinical trials. Conflicts of interest are a significant concern.
- Nutrition and dietary studies: This field is heavily influenced by food industry interests, fad diets, and ideological biases. Poorly designed studies with small sample sizes or lack of control groups are common. Results are also frequently sensationalized for marketing purposes.
- Environmental and climate science: While the core science is sound, research in these areas can face political pressure, industry lobbying, or ideological opposition that leads to cherry-picking data, misrepresenting findings, or questioning well-established conclusions for vested interests.
- Psychology and social sciences: Replication issues, small sample sizes, lack of effective blinding, and selective reporting have been problems. The desire for attention-grabbing findings can incentivize questionable practices.
- Alternative medicine and fringe fields: Studies in these domains frequently lack scientific rigor, rely on anecdotal evidence, make unsupported claims, and do not follow standards of evidence-based research. There are also financial motivations at play.
Broadly speaking, factors that can drive the abandonment of proper scientific methods include:
1) Financial interests and profit motives, leading to biased or unethical research practices.
2) Political or ideological pressures, causing selective interpretation or suppression of findings.
3) Desire for attention, recognition or to confirm pre-existing beliefs.
4) Poor research training, lack of understanding of scientific principles.
5) Absence of rigorous peer review and oversight in certain fields or publications.
Ultimately, the self-correcting nature of science and adherence to principles like transparency, reproducibility, and objective evidence-based reasoning are crucial safeguards against the corruption or abandonment of proper scientific practices.
Provide an extensive list of questions we should ask whenever a scientific claim is made.
Questions to Ask When Evaluating a Scientific Claim
When encountering a scientific claim, it’s crucial to critically evaluate the information before accepting it as valid. Here’s an extensive list of questions designed to help scrutinize the reliability and integrity of scientific assertions:
Source and Credibility
- Who is making the claim?
- What are their qualifications and expertise in the field?
- Do they have any potential conflicts of interest?
- Is the claim supported by a reputable institution or journal?
Evidence and Methodology
- What evidence is presented to support the claim?
- Is the underlying research published in a peer-reviewed journal?
- What methods were used to gather data and conduct the research?
- Were the study’s methods appropriate to address the specific questions or hypotheses?
- Was the sample size adequate to draw the conclusions presented?
- Were the study participants or subjects representative of the population?
- Were there any control groups used in the study?
- Was the study observational or experimental, and what are the implications of this for the claim?
- Were all relevant variables controlled or accounted for in the research?
Reproducibility and Consistency
- Have similar results been reported in other studies?
- Can the results be replicated by independent researchers using the same methods?
- Has there been any significant criticism or controversy regarding the research?
Transparency and Openness
- Is the full research paper accessible for review?
- Are the data and methodology openly available for scrutiny?
- Has the research been retracted, corrected, or updated since its initial publication?
Rationality and Reasoning
- Does the claim align logically with existing scientific knowledge?
- Are the conclusions drawn from the evidence reasonable and justified?
- Does the claim involve extrapolations that are not supported by the data?
- Are there alternative explanations for the findings?
- How does the claimant address opposing viewpoints or contradictory evidence?
Impact and Relevance
- What implications does the claim have if true?
- How does the claim affect existing theories and knowledge?
- Is the claim being reported by the media accurately?
- What are the potential benefits and risks associated with the claim?
- How is the claim relevant to policy, personal decisions, or broader societal issues?
By asking these questions, you can better assess the validity of scientific claims and distinguish between well-founded conclusions and those that might be questionable or misleading.
Here’s an extensive list of questions to ask whenever a scientific claim is made:
Source and Origin:
- Who is making the claim? Are they a qualified scientist with expertise in the relevant field?
- Where is the claim coming from? Is it a scientific journal, a news article, a website, or a social media post?
- Is the source reputable? For scientific claims, look for research published in peer-reviewed journals. Websites and social media posts need to be critically evaluated for their credibility.
Evidence and Data:
- What evidence is used to support the claim? Is it based on data from well-designed studies?
- How strong is the evidence? Is the sample size large enough? Were control groups used? Was the study double-blinded?
- Has the research been replicated by other scientists? Credible scientific findings can be reproduced using similar methods.
- Are there alternative explanations for the findings? Consider the possibility of correlation not equaling causation.
Reasoning and Interpretation:
- How is the data being interpreted? Is it a reasonable interpretation of the evidence, or is there a possibility of bias or cherry-picking data?
- Are there any logical fallacies in the reasoning used to support the claim?
- Do the conclusions logically follow from the evidence presented?
Context and Implications:
- What is the context of the claim? Are there any relevant factors that are not being considered?
- What are the potential implications of the claim? Could it have a significant impact on public health, policy, or the environment?
- Are there any ethical considerations related to the research?
Additional Considerations:
- Is the claim being presented in a sensationalized way? Beware of exaggerated headlines or claims that seem too good to be true.
- Who might benefit from this claim being widely accepted? Consider potential conflicts of interest.
- Can you find information from other reputable sources that contradict this claim?
Remember:
- It’s okay to be skeptical! Asking questions is a crucial part of scientific thinking.
- Don’t be afraid to admit that you don’t know something. Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving.
- There are many resources available to help you evaluate scientific claims. Consult websites from reputable scientific organizations, universities, or libraries.
By asking these questions, you can become a more informed and critical consumer of scientific information.
When evaluating any scientific claim, it’s important to ask probing questions to assess its validity, reliability, and adherence to scientific principles. Here’s an extensive list of questions we should consider asking:
- What is the source of the claim? Is it from a reputable scientific institution, peer-reviewed journal, or credible researcher?
- Who conducted the research, and what are their qualifications and potential conflicts of interest?
- What is the specific question or hypothesis being investigated?
- What methodology was used to conduct the research (e.g., experimental design, observational study, modeling)?
- How large and representative was the sample size, and how were the subjects or data points selected?
- Was there an appropriate control group or baseline for comparison?
- Were the experiments or observations conducted under controlled conditions?
- Were the researchers and participants blind to the treatment or intervention (double-blind study)?
- How were variables measured, and were the measurements accurate and precise?
- Were there any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that could have influenced the results?
- Were the statistical analyses appropriate and properly conducted?
- Are the reported results statistically significant, and what is the margin of error or confidence interval?
- Have the findings been replicated by independent researchers or under different conditions?
- Do the conclusions logically follow from the data and findings, or are they overreaching?
- Are there any alternative explanations or hypotheses that could account for the results?
- How do the findings fit within the broader context of existing scientific knowledge and theories?
- Have the researchers addressed potential limitations or weaknesses of their study?
- Has the research been peer-reviewed and scrutinized by independent experts in the field?
- Are there any conflicts of interest, ideological biases, or vested interests that could have influenced the research?
- Are there any ethical concerns or violations regarding the research methodology or treatment of subjects?
These questions cover various aspects of scientific research, including the credibility of sources, study design, methodology, data analysis, replication, peer review, and potential biases or limitations. Critically examining these factors can help separate well-conducted, reliable scientific studies from those that may be flawed, pseudoscientific, or driven by agendas other than the pursuit of objective truth.
Create a 10-item quiz on the entire thread above.
Quiz on Evaluating Scientific Claims and Spotting Bad Science
- What is a common issue in pharmaceutical research that can lead to abandoning proper scientific methods?
- Why is sample size important in scientific studies?
- What is meant by “conflicts of interest” in the context of scientific research?
- What does it mean when research results are not replicable?
- How does media influence potentially affect the reporting of scientific findings?
- What is the significance of using a control group in scientific experiments?
- What type of testing helps prevent bias in scientific studies by ensuring neither the subjects nor the researchers know who is receiving a particular treatment?
- What term is used to describe the practice of selecting data that supports one’s hypothesis while ignoring data that does not?
- In what way can financial incentives impact the integrity of scientific research?
- Why is peer review an important part of the scientific process?
Answers to the Quiz
- Publication bias and data manipulation due to financial incentives.
- Larger and more diverse sample sizes provide more reliable and generalizable results.
- It refers to situations where personal or financial interests might affect a researcher’s actions or decisions.
- It means the study’s findings cannot be duplicated by other researchers using the same methods, possibly indicating flaws in the original study.
- It can lead to the sensationalization of scientific findings or the misrepresentation of the research to attract more attention.
- It allows researchers to compare outcomes and determine the effects of the variable being tested.
- Double-blind testing.
- Cherry-picking.
- It can lead to biased results and a preference for positive outcomes that are more likely to secure funding or approval.
- It ensures that research is critically evaluated by other experts in the field before it is published, helping to maintain quality and credibility.
Quiz: Evaluating Scientific Claims
Test your knowledge on how to approach scientific claims with a critical eye.
- According to the passage, which of the following is a potential consequence of research with a strong financial motive?
- What is a key feature of a well-designed scientific study, as discussed in the passage?
- When evaluating a scientific claim, why is it important to consider the source of the information?
- Biases in scientific research can be driven by factors like what, according to the passage?
- The passage suggests that credible scientific findings should be _______ by other researchers.
- Anecdotal evidence, such as personal experiences, is considered to be a form of strong scientific evidence according to the passage. (True or False)
- When a scientific claim seems sensationalized or too good to be true, what does the passage recommend?
- In the context of scientific claims, what is the potential danger of “cherry-picking” data?
- According to the passage, what is an important step in the scientific process that helps ensure the reliability of research?
- When encountering a scientific claim, the passage suggests it’s best to: (a) Accept it at face value, (b) Approach it with a critical and questioning mind, (c) Only trust claims from scientists you personally know.
Answers:
- (c) Prioritizing commercial interests over rigorous methodology
- (b) Using control groups
- (a) To determine the credibility and expertise behind the claim
- (b) Financial gain and ideological biases
- (a) Replicated
- (False) Anecdotal evidence is not considered strong scientific evidence.
- (c) Be wary of it and seek information from reputable sources.
- (a) It can lead to misleading conclusions that don’t represent the full picture.
- (c) Peer review
- (b) Approach it with a critical and questioning mind
Here’s a 10-item quiz on the content covered in this thread:
- According to the image, what issue does the point “Sensationalised Headlines” refer to?
- True or False: The image suggests that companies or researchers may have personal or financial interests that could bias their research.
- What term is used in the image to describe the mistake of assuming that correlation implies causation?
- According to the image, what is a potential issue with small sample sizes in studies?
- The image mentions the importance of having an appropriate control group in what type of study?
- What measure is suggested by the image to help prevent bias from influencing study outcomes?
- Which point in the image refers to the practice of selectively reporting data that supports a desired conclusion while ignoring contradictory evidence?
- According to the discussion, what domain of science is particularly susceptible to abandoning proper methods due to profit motivations and financial interests?
- The thread suggests that which factor can drive the abandonment of proper scientific practices?
- In the list of questions to ask when evaluating scientific claims, what aspect is covered by the question: “Have the findings been replicated by independent researchers or under different conditions?”
Answers:
- Scientific findings are often sensationalized in news headlines to attract readers, exaggerating or misrepresenting the actual research conclusions.
- True
- Correlation & Causation
- Small sample sizes can limit the confidence in the results.
- Clinical trials
- Blind testing
- Selective Reporting of Data (also known as “cherry-picking”)
- Medical and pharmaceutical research
- Financial interests and profit motives
- Replicability of the findings
Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.
Discussion Questions on Evaluating Scientific Claims and Spotting Bad Science
- How do sensationalized headlines affect public perception of science and what steps can be taken to mitigate this effect?
- Discuss the potential consequences of conflicts of interest in scientific research. How can these be more effectively disclosed and managed?
- How might the pressure to publish affect the quality and integrity of scientific research?
- In what ways do financial incentives potentially compromise the objectivity of pharmaceutical research?
- Discuss the challenges and implications of replicating psychological studies. What solutions might improve replicability in this field?
- How does the lack of a control group in an experimental study undermine the validity of the results?
- What are the ethical considerations involved in blind and double-blind testing in clinical trials?
- Discuss the impact of cherry-picking data on the credibility of scientific research. How can this practice be identified and discouraged?
- How can journalists improve their reporting on scientific studies to avoid misinterpreting or oversimplifying the findings?
- What role does peer review play in maintaining the quality of scientific publications? Discuss its strengths and weaknesses.
- How does the complexity of environmental variables challenge the methodologies of environmental science research?
- Discuss how ideological biases might influence economic studies and the interpretation of their results.
- In what ways can open access to research data and methodologies benefit the scientific community and the public?
- What strategies can be employed to educate the public on the importance of critical thinking when evaluating scientific claims?
- How can policymakers use scientific findings effectively when there is controversy or debate surrounding the research?
These questions can serve as a basis for deepening understanding and stimulating thoughtful discussion on the practices, challenges, and ethical considerations in the field of scientific research.
Discussion Questions: Evaluating Scientific Claims
- Have you ever encountered a scientific claim that seemed too good to be true? How did you evaluate its credibility?
- Why do you think it’s important for the general public to be able to critically evaluate scientific claims?
- In your opinion, what are some of the biggest challenges people face when trying to distinguish between credible science and pseudoscience?
- How can social media platforms play a role in spreading misinformation about science?
- What are some strategies we can use to become more informed consumers of scientific information online?
- The passage mentions “confirmation bias.” Can you think of any examples from your own life where this might have influenced your perception of a scientific claim?
- Do you think there’s a role for scientists to play in communicating complex scientific concepts to the public in a clear and understandable way? Why or why not?
- How can science education be improved to better equip students with the skills to critically evaluate scientific claims?
- In the context of the passage, how can scientific institutions ensure that research is conducted ethically and without undue influence from financial interests?
- With the constant flow of new scientific discoveries, how can we stay up-to-date on scientific advancements without getting overwhelmed by information?
- The passage talks about peer review. Can you think of any potential limitations of the peer-review process?
- Scientific research often involves complex terminology. How can this be a barrier to public understanding of science?
- Can you think of any examples in history where scientific discoveries were met with skepticism or resistance? What factors might contribute to this?
- How can scientific literacy help us make informed decisions about our health and well-being?
- In your opinion, how can we foster a culture of curiosity and critical thinking when it comes to scientific claims in society?
Here are 15 discussion questions relevant to the content covered in this thread:
- Can you think of any recent examples of sensationalized headlines or misrepresented scientific findings in the media?
- How can personal or financial conflicts of interest influence the objectivity and integrity of scientific research?
- What are some examples of commonly misunderstood correlations that are mistaken for causal relationships?
- Why is it important to have representative and sufficiently large sample sizes in scientific studies?
- In what cases might it be acceptable or necessary to conduct a study without a control group, and what are the potential limitations?
- How does blind testing help to reduce bias in scientific experiments, and are there situations where it may not be feasible or ethical?
- Can you think of any instances where selective reporting of data or “cherry-picking” may have led to misleading conclusions in a particular field of study?
- What measures can be taken to ensure transparency and accountability in scientific research, particularly in fields with strong financial interests or motives?
- How does the peer-review process help to maintain the integrity and quality of scientific publications?
- What role do replication studies play in validating or questioning previous scientific findings?
- Can you think of any examples of pseudoscientific claims or practices that fail to meet the standards of evidence-based research?
- How can ideological biases or preexisting beliefs influence the interpretation and acceptance of scientific evidence?
- What are some potential ethical concerns or violations that can arise in the conduct of scientific research, particularly involving human subjects?
- How can the public and policymakers better differentiate between well-conducted, reliable scientific studies and those that may be flawed or driven by agendas?
- What measures can be taken to improve scientific literacy and critical thinking skills, enabling people to evaluate scientific claims more effectively?
Table of Contents: (Click any link below to navigate to that section.)
- Elaborate on each of the 12 points in this image.
- Elaborate on the 12 Points on Spotting Bad Science
- 1. Sensationalized Headlines
- 2. Misinterpreted Results
- 3. Conflicts of Interest
- 4. Correlation & Causation
- 5. Unsupported Conclusions
- 6. Problems with Sample Size
- 7. Unrepresentative Samples Used
- 8. No Control Group Used
- 9. No Blind Testing Used
- 10. Selective Reporting of Data
- 11. Unreplicable Results
- 12. Non-Peer Reviewed Material
- Elaborate on the 12 Points on Spotting Bad Science
- Which domains of science are most susceptible to the abandonment of proper science, and what commonly drives its abandonment?
- Provide an extensive list of questions we should ask whenever a scientific claim is made.
- Create a 10-item quiz on the entire thread above.
- Provide 15 discussion questions relevant to the content above.






Leave a comment